3.14-15
Hacks and Notes
Notes and Takeaways
- Existing code segments can be derived from existing sources
- Libraries can be used to simplify complex programs
- Libraries are collections of pre-written code or procedures that can be used to maximize efficiency
- Documentation is explaining what the procedure/code does
- random(a, b) returns a random integer between a and b
- random.choice will pick a random item from a list of strings
- random.shuffle will shuffle a list
- randint is random integer
- randrange picks from a range of numbers which have a certain start value and multiple
- Overall, utilizing libraries such as the random one can make it much easier to code and allow you do more things than you normally would with your code
Reflection
I learned the importance of libraries and how to use them, specifically the random function, which you can do a lot more stuff with than I realized. I know there is a lot more libraries which have a lot more functions, and I plan on researching some of them so that I can do a lot more with my code while still keeping it relatively simple.
Multiple Choice
-
What does the random(a,b) function generate?
A. A random integer from a to be exclusive
B. A random integer from a to b inclusive.
C. A random word from variable a to variable b exclusive.
D. A random word from variable a to variable b inclusive.
I chose B because it includes the integers listed and it is not in reference to variables. a and b are just place holders for integers you would put on the list
-
What is x, y, and z in random.randrange(x, y, z)?
A. x = start, y = stop, z = step
B. x = start, y = step, z = stop
C. x = stop, y = start, z = step
D. x = step, y = start, z = stop
I chose A because x and y reference the start and stop of the range you want to pull from and z is the step, or the number you are adding by
-
Which of the following is NOT part of the random library?
A. random.item
B. random.random
C. random.shuffle
D. random.randint
I chose A because all the other ones have particular functions. I initially got “random.item” confused with “random.choice”. I also initially thought it was random.random, but I found out that can find a random floating point
Short Answer Questions
- What is the advantage of using libraries?
- It allows us to import code that as already written/developed and can make it a lot easier to code certain algorithms/procedures, as well as allowing us to a lot more with our code
- Write a thorough documentation of the following code.
import random
names_string = input("Give me everybody's names, seperated by a comma.")
names = names_string.split(",")
num_items = len(names)
random_choice = random.randint(0, num_items - 1)
person_who_will_pay = names[random_choice]
print(f"{person_who_will_pay} is going to buy the meal today!")
Documentation: This code builds a list of names based on the user input and then chooses a random name from the list to decide who is going to pay for the meal.
Coding Challenges
Jupyter notebooks aren’t working with fastpages so I’m just going to show screenshots of my code/outputs
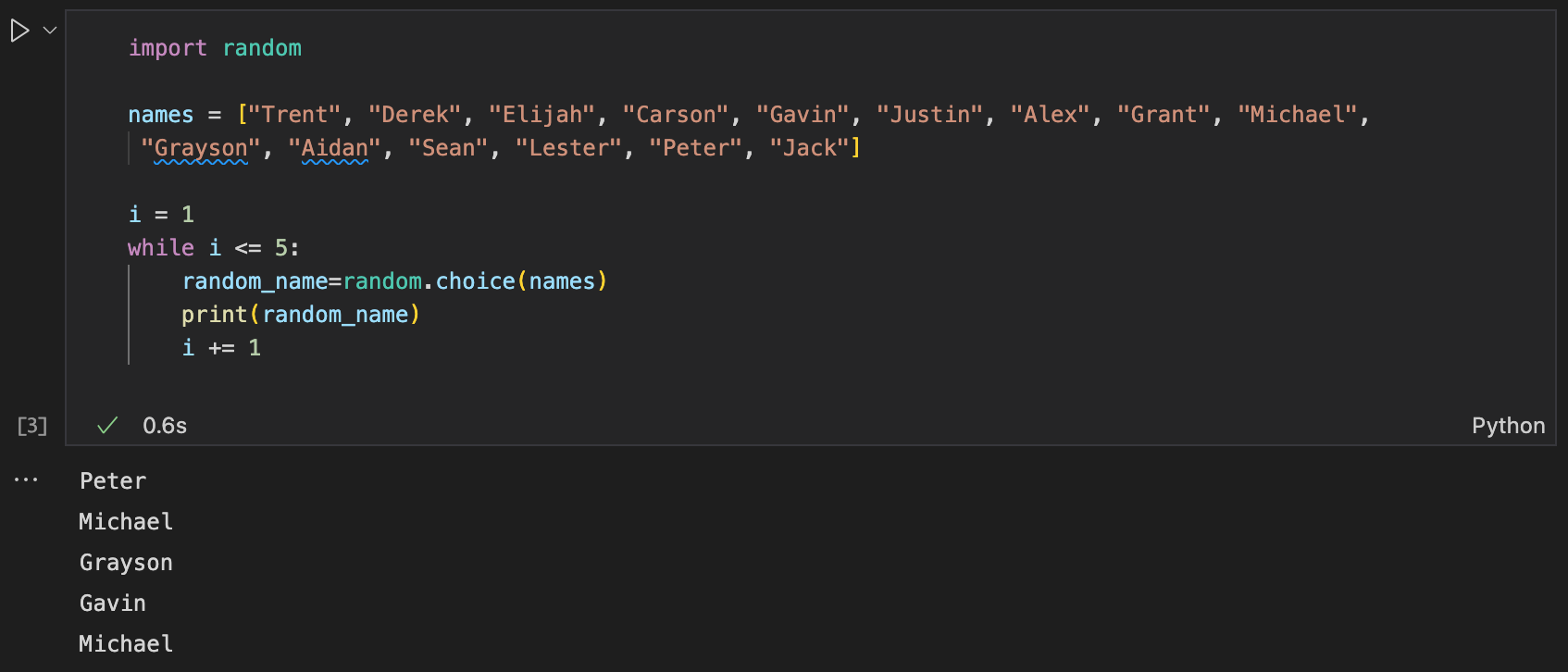
- Create a program to pick five random names from a list of at least 15 names
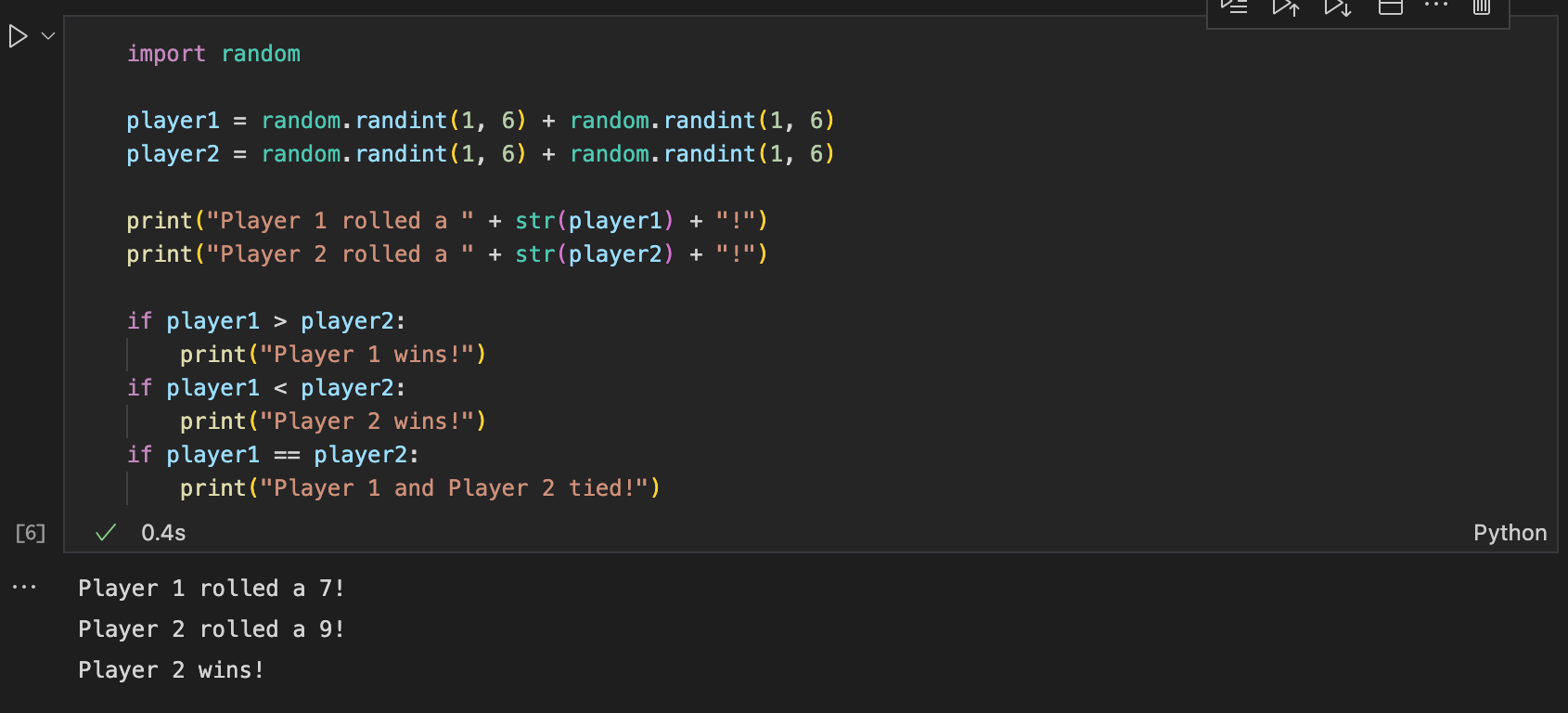
- Create a program to simulate a dice game where each player rolls two fair dice (6 sides); the player with the greater sum wins
Extra Credit
I tried my best, but I wasn’t sure how to make it completely mutually exclusive so if an obstacle complicated with something else than I just got rid of that obstacle
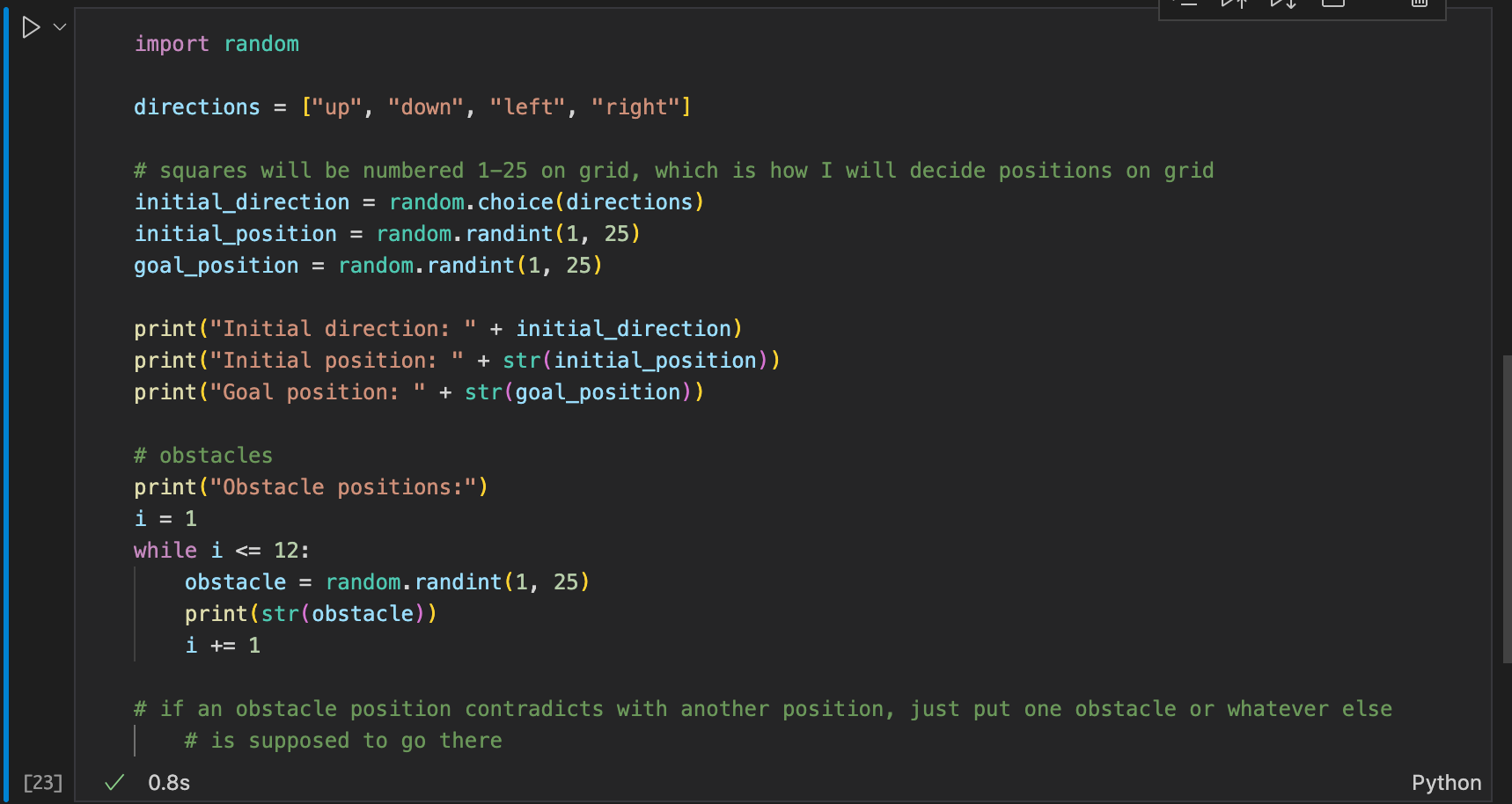

Here’s my illustration using the numbers generated from the code: