Data Structures- Hashmaps, Sets, Hash Tables, Hashing and Collisions
Observing hashmaps with python dictionaries
- What is a Hashtable/Hashmap?
- What is Hashing and Collision?
- What is a Set?
- Dictionary Example
- Hacks
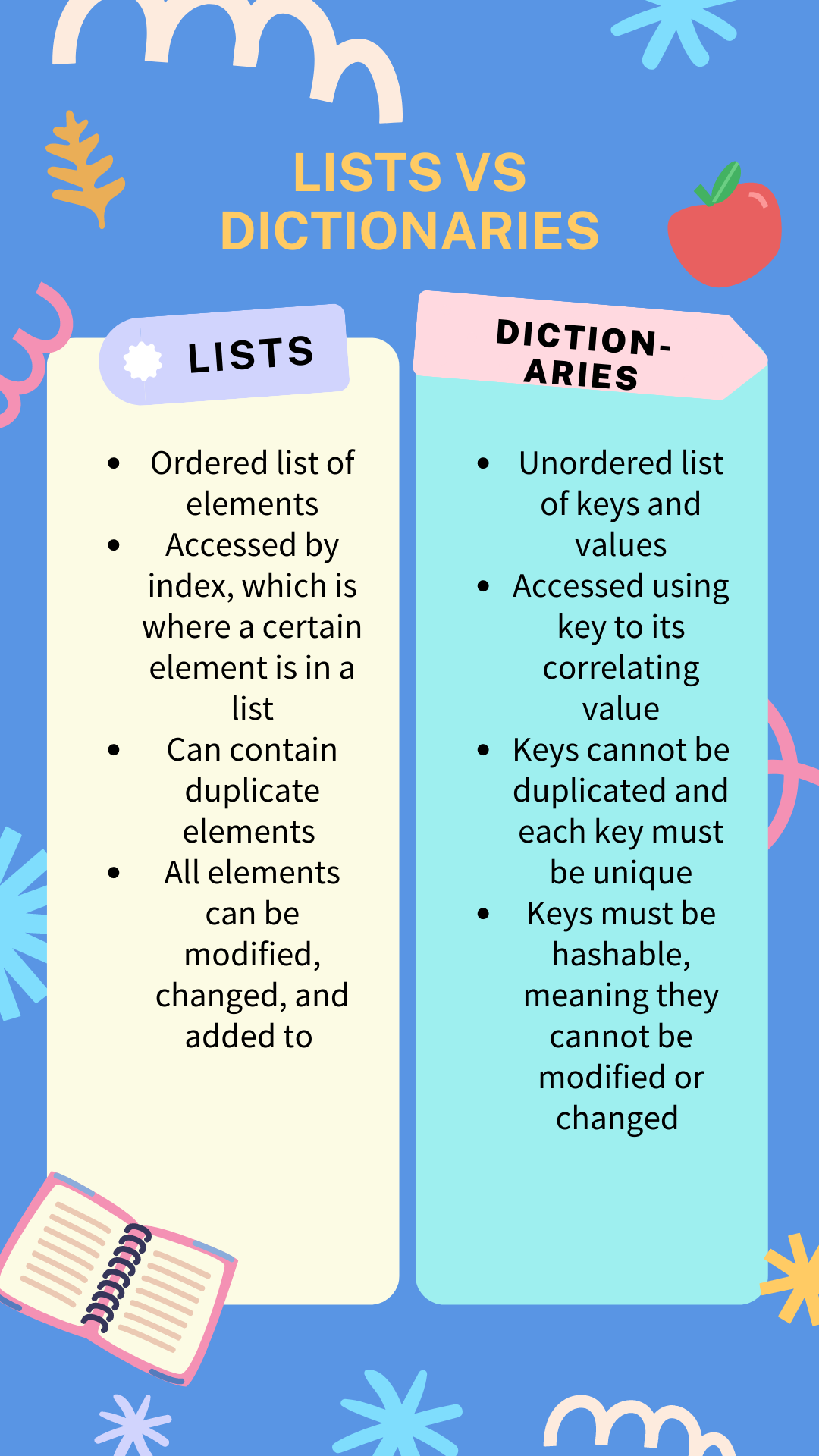
- Canva Comparison
What is a Hashtable/Hashmap?
A hashtable is a data structure that with a collection of key-value pairs, where each key maps to a value, and the keys must be unique and hashable.
- In Python there is a built in hashtable known as a ___.
The primary purpose of a hashtable is to provide efficient lookup, insertion, and deletion operations. When an element is to be inserted into the hashtable, a hash function is used to map the key to a specific index in the underlying array that is used to store the key-value pairs. The value is then stored at that index. When searching for a value, the hash function is used again to find the index where the value is stored.
The key advantage of a hashtable over other data structures like arrays and linked lists is its average-case time complexity for lookup, insertion, and deletion operations.
- The typical time complexity of a hashtable is ___.
What is Hashing and Collision?
Hashing is the process of mapping a given key to a value in a hash table or hashmap, using a hash function. The hash function takes the key as input and produces a hash value or hash code, which is then used to determine the index in the underlying array where the value is stored. The purpose of hashing is to provide a quick and efficient way to access data, by eliminating the need to search through an entire data structure to find a value.
However, it is possible for two different keys to map to the same hash value, resulting in a collision. When a collision occurs, there are different ways to resolve it, depending on the collision resolution strategy used.
Python's dictionary implementation is optimized to handle collisions efficiently, and the performance of the dictionary is generally very good, even in the presence of collisions. However, if the number of collisions is very high, the performance of the dictionary can degrade, so it is important to choose a good hash function that minimizes collisions when designing a Python dictionary.
What is a Set?
my_set = set([1, 2, 3, 2, 1])
print(my_set)
# What do you notice in the output?
# It doesn't print any duplicates. It only prints each number involved once, even if it is mentioned
# multiple times
# Why do you think Sets are in the same tech talk as Hashmaps/Hashtables?
# Like hashmaps and hashtables, sets have unique values
#
lover_album = {
"title": "Lover",
"artist": "Taylor Swift",
"year": 2019,
"genre": ["Pop", "Synth-pop"],
"tracks": {
1: "I Forgot That You Existed",
2: "Cruel Summer",
3: "Lover",
4: "The Man",
5: "The Archer",
6: "I Think He Knows",
7: "Miss Americana & The Heartbreak Prince",
8: "Paper Rings",
9: "Cornelia Street",
10: "Death By A Thousand Cuts",
11: "London Boy",
12: "Soon You'll Get Better (feat. Dixie Chicks)",
13: "False God",
14: "You Need To Calm Down",
15: "Afterglow",
16: "Me! (feat. Brendon Urie of Panic! At The Disco)",
17: "It's Nice To Have A Friend",
18: "Daylight"
}
}
# What data structures do you see?
# List on genre, and tracks have a dictionary
#
# Printing the dictionary
print(lover_album)
print(lover_album.get('tracks'))
# or
print(lover_album['tracks'])
print(lover_album.get('tracks')[4])
# or
print(lover_album['tracks'][4])
lover_album["producer"] = set(['Taylor Swift', 'Jack Antonoff', 'Joel Little', 'Taylor Swift', 'Louis Bell', 'Frank Dukes'])
# What can you change to make sure there are no duplicate producers?
# Make it into a set
#
# Printing the dictionary
print(lover_album)
lover_album["tracks"].update({19: "All Of The Girls You Loved Before"})
lover_album["genre"].append("electropop")
# How would add an additional genre to the dictionary, like electropop?
# Since genre is a list, use the append function to add something else to the list
#
# Printing the dictionary
print(lover_album)
def display_album(album):
# Print lover_album in more readable format
for k,v in album.items(): # iterate using a for loop for key and value
print(str(k) + ": " + str(v))
if k == "genre": # have iteration stop before it reaches "tracks"
break
# print "tracks" in more readable format
print("tracks:")
for k,v in album["tracks"].items():
print("\t" + str(k) + ": " + str(v))
# Write your own code to print tracks in readable format
# I made the first loop stop at "genre" then made a second for loop just for the tracks section
#
display_album(lover_album)
def search():
search = input("What would you like to know about the album?")
if lover_album.get(search.lower()) == None:
print("Invalid Search")
else:
print(lover_album.get(search.lower()))
search()
# This is a very basic code segment, how can you improve upon this code?
# You can add to search for specific tracks or
#
Hacks
- Answer ALL questions in the code segments
- Create a diagram or comparison illustration (Canva).
- What are the pro and cons of using this data structure?
- Dictionary vs List
- Expand upon the code given to you, possible improvements in comments
-
Build your own album showing features of a python dictionary
-
For Mr. Yeung's class: Justify your favorite Taylor Swift song, answer may effect seed
def update():
track = len(lover_album["tracks"]) + 1
name = input("Enter the name for the new track:")
lover_album["tracks"].update({track: name})
update()
display_album()
def delete():
track = input("Which track # do you want to delete?")
lover_album["tracks"].pop(track)
display_album()
delete()
album = {}
title = input("What do you want your album to be called?")
album.update({"title": title})
artist = input("Who is this album by?")
album.update({"artist": artist})
genre = input("What genre is this album?")
album.update({"genre": [genre]})
track = input("What will be the name of the first track on this album")
album.update({"tracks": {1: track}})
def more_tracks():
msg = input("Will there be more tracks on this album? Enter y for yes and n for no")
if msg == "y":
num = len(album["tracks"]) + 1
tracks = input("What will be the name of the next track on the album")
album["tracks"].update({num: tracks})
more_tracks()
if msg == "n":
display_album(album)
more_tracks()